data(cigdata)
x <- cigdata$cigtax
y <- cigdata$cigsales
beta_hat <- cov(x, y) / var(x)
alpha_hat <- mean(y) - beta_hat * mean(x)
c(alpha_hat, beta_hat)[1] 55.948902 -9.487131Week 13
Textbook Reference: JA Chapter 17
\[ Y_i = \alpha + \beta X_i + U_i \]
where
Assumption: \(E[U_i|X_i] = 0\) ensures unbiased estimation.
Goal: minimize the Sum of Squared Residuals
\[ S(\alpha,\beta)=\sum_i (Y_i - \alpha - \beta X_i)^2 \]
First-order conditions:
\[ \frac{\partial S}{\partial \alpha}=0,\quad \frac{\partial S}{\partial \beta}=0 \]
Solution:
\[ \hat{\beta}=\frac{\sum_i (X_i-\bar{X})(Y_i-\bar{Y})}{\sum_i (X_i-\bar{X})^2},\qquad \hat{\alpha}=\bar{Y}-\hat{\beta}\bar{X}. \]
data(cigdata)
x <- cigdata$cigtax
y <- cigdata$cigsales
beta_hat <- cov(x, y) / var(x)
alpha_hat <- mean(y) - beta_hat * mean(x)
c(alpha_hat, beta_hat)[1] 55.948902 -9.487131lm() in Rmodel <- lm(cigsales ~ cigtax, data = cigdata)
summary(model)
Call:
lm(formula = cigsales ~ cigtax, data = cigdata)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-23.921 -8.098 -0.857 5.014 39.338
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 55.949 3.244 17.249 < 2e-16 ***
cigtax -9.487 1.511 -6.277 8.75e-08 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 12.52 on 49 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.4457, Adjusted R-squared: 0.4344
F-statistic: 39.4 on 1 and 49 DF, p-value: 8.754e-08Interpretation:
- Intercept (\(\hat{\alpha}\)) – predicted sales if tax = 0
- Slope (\(\hat{\beta}\)) – change in sales per $1 increase in tax
ggplot(cigdata, aes(x=cigtax, y=cigsales)) +
geom_point(color="grey40") +
geom_smooth(method="lm", se=FALSE, color="blue") +
labs(title="Cigarette Sales vs Tax per Pack",
subtitle="OLS fitted line",
x="Tax per pack (USD)", y="Cigarette sales per capita")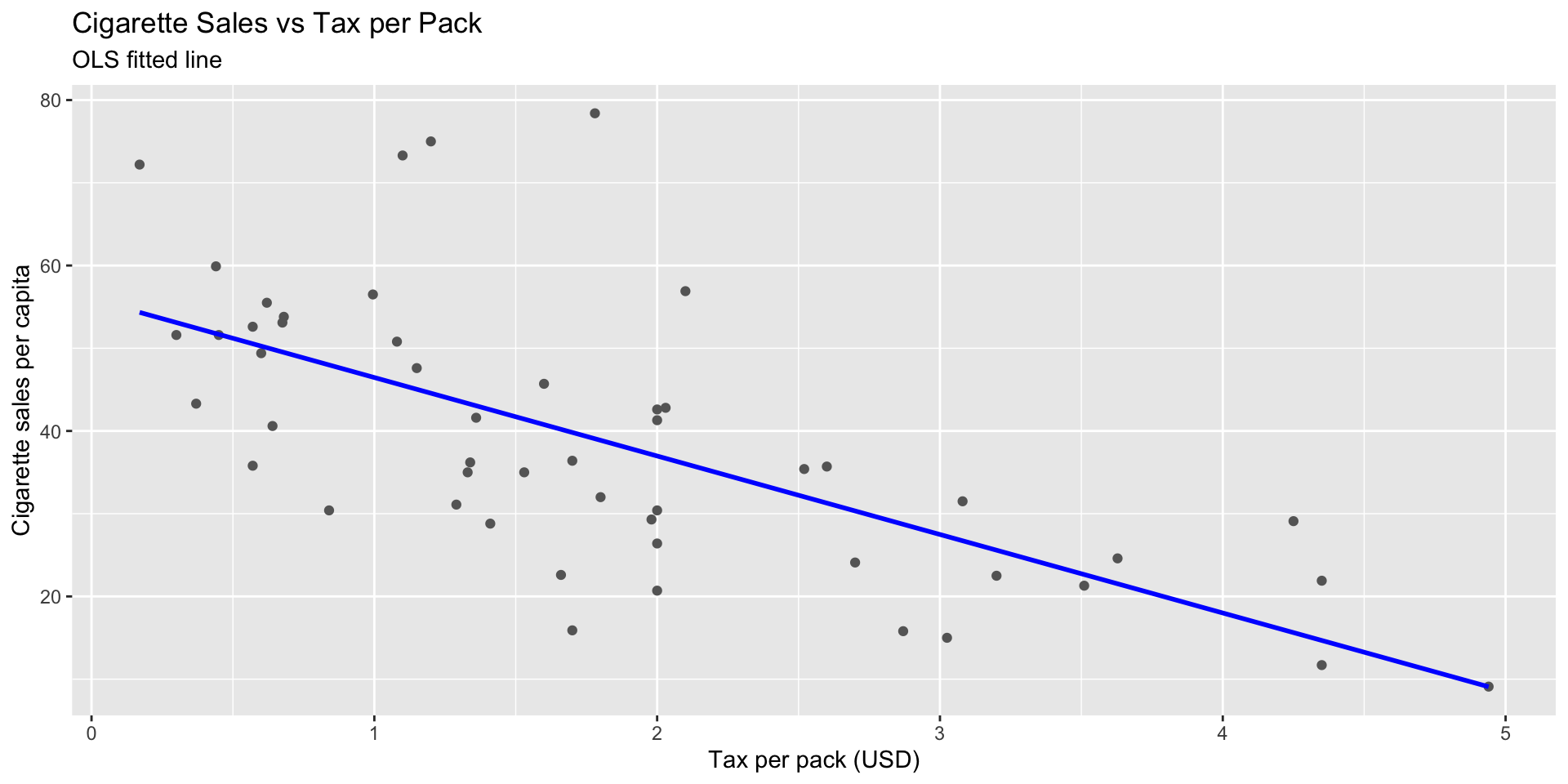
cigdata <- cigdata |>
mutate(fitted = fitted(model),
resid = resid(model))
ggplot(cigdata, aes(x=cigtax, y=cigsales)) +
geom_point(color="grey60") +
geom_segment(aes(xend=cigtax, yend=fitted), color="red", alpha=0.5) +
geom_smooth(method="lm", se=FALSE, color="blue") +
labs(title="Residuals as Vertical Deviations",
subtitle="Each residual is ŷᵢ − yᵢ",
x="Tax per pack (USD)", y="Cigarette sales per capita")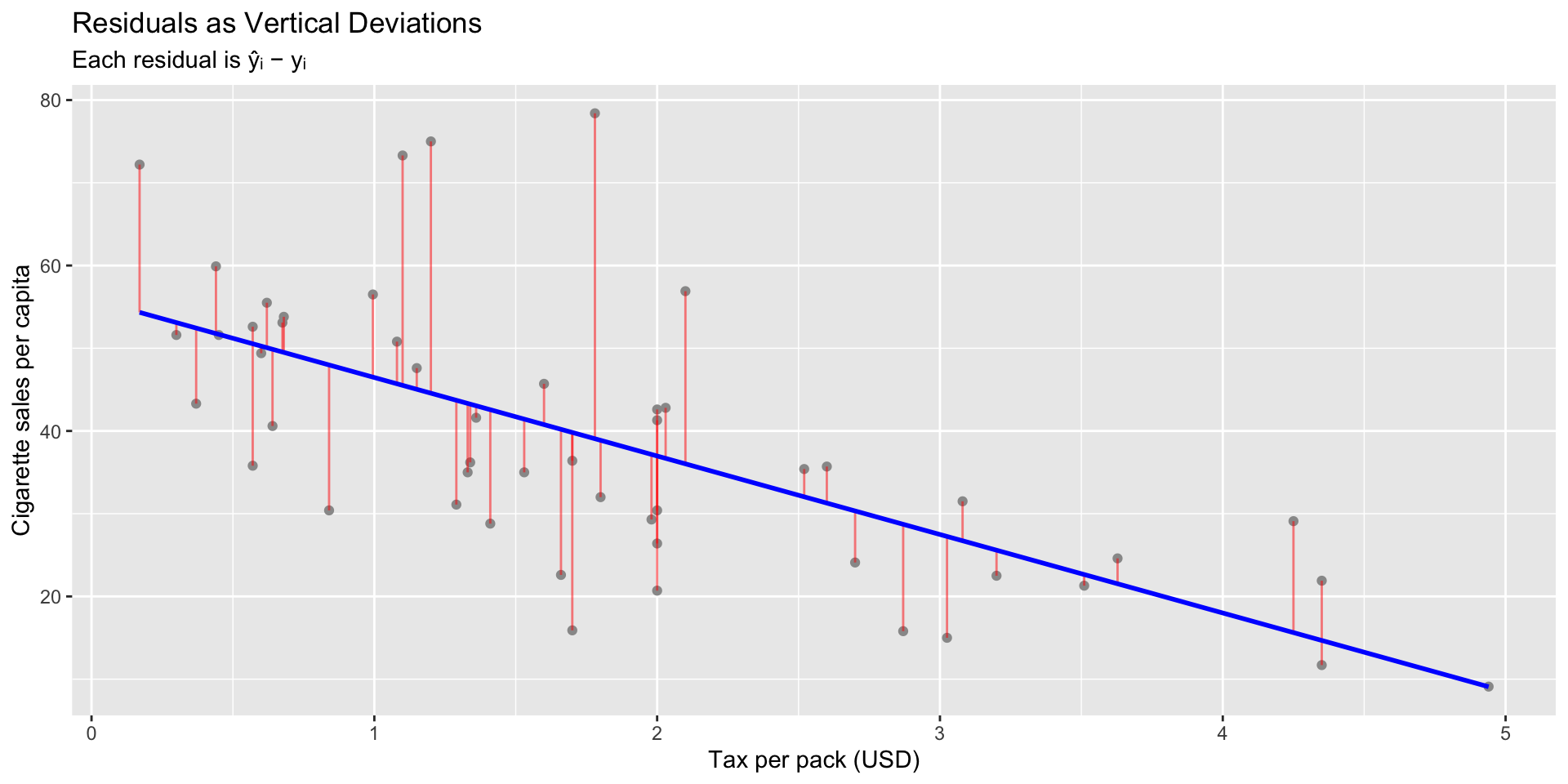
\[ \sum_i \hat{u}_i = 0,\quad \sum_i X_i \hat{u}_i = 0. \]
| Prediction | Causality |
|---|---|
| Goal: minimize prediction error | Goal: estimate causal effect |
| Focus on fit \(E[Y|X]\) | Requires \(E[U|X]=0\) |
| Works with any \(X\)–\(Y\) relation | Needs exogenous variation |
| “What \(Y\) do I expect if \(X = x\)?” | “What happens to Y if I change X?” |
When assumptions hold:
\[ t = \frac{\hat{\beta} - \beta_0}{se(\hat{\beta})} \quad \sim \; t_{n-2}. \]
Use summary(model) in R to see \(t\) statistic and p-value.
cigsales on cigtax, interpret the slope’s sign and magnitude.Under what condition can the regression coefficient \(\beta\) be interpreted as a causal effect?
Only if the exogeneity condition \(E[U|X]=0\) holds — that is, when changes in \(X\) are not systematically related to the unobserved factors \(U\).